Fields of application
The block-oriented simulation system BORIS is the basic module of WinFACT. Due to its concept, it is not only predestinated for an application as a simulation tool but can also be applied in the fields of recording and processing of measured data and control.
In contrast to traditional simulation systems, BORIS allows the direct integration of fuzzy and neuro systems in the simulation process and, thus, is suitable specially for applications in the field of fuzzy logic and fuzzy control. In addition to the simulation itself, system structures designed with BORIS can be precompiled to ANSI-C-Code with the help of the AutoCode-Generators.
Beyond its application as a pure software tool, BORIS offers numerous possibilities of hardware connecting. In connection with A/D-D/A-cards or external hardware modules it is possible to realize a direct process interfacing which allows to test a control system that has been projected with a PC. A later transfer to the target hardware can, on one hand, be achieved via C-code-generation and, on the other hand, via the WinFACT micro-controller system.
Configuring the system structure
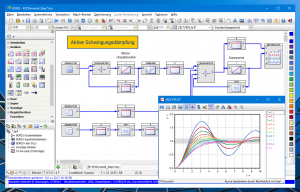
The simulation structure can be simply configurated by placing system specific icons to any place at the screen and by connecting them with a mouse click. The integrated autorouter (which naturally can be deactivated) is able to position the connections automatically and in the best possible manner. If desirable, connections can be drawn with user defined colors. The virtual worksheet can be scrolled thus enabling a clear and extremely fast structuring of even complex systems. A structure overview window allows the display of the whole system structure at any time. The complexity of the system structure is only restricted by the memory capacity of the PC.
Simulation control
BORIS offers various modes for the control of the simulation process. Some features in brief:
- Standard- and Endless-Simulation
- Single Step Mode (manually activated or by process)
- Breakpoints
- Real Time Simulation
- Automatic Overflow Check
- System State Snap
The simulation process is documented within the status bar. Important especially for debugging purposes is the possibility to display all actual block output values within the block caption if desired. A choice of several numerical integration methods is available for the simulation itself.
The System Block Library of BORIS
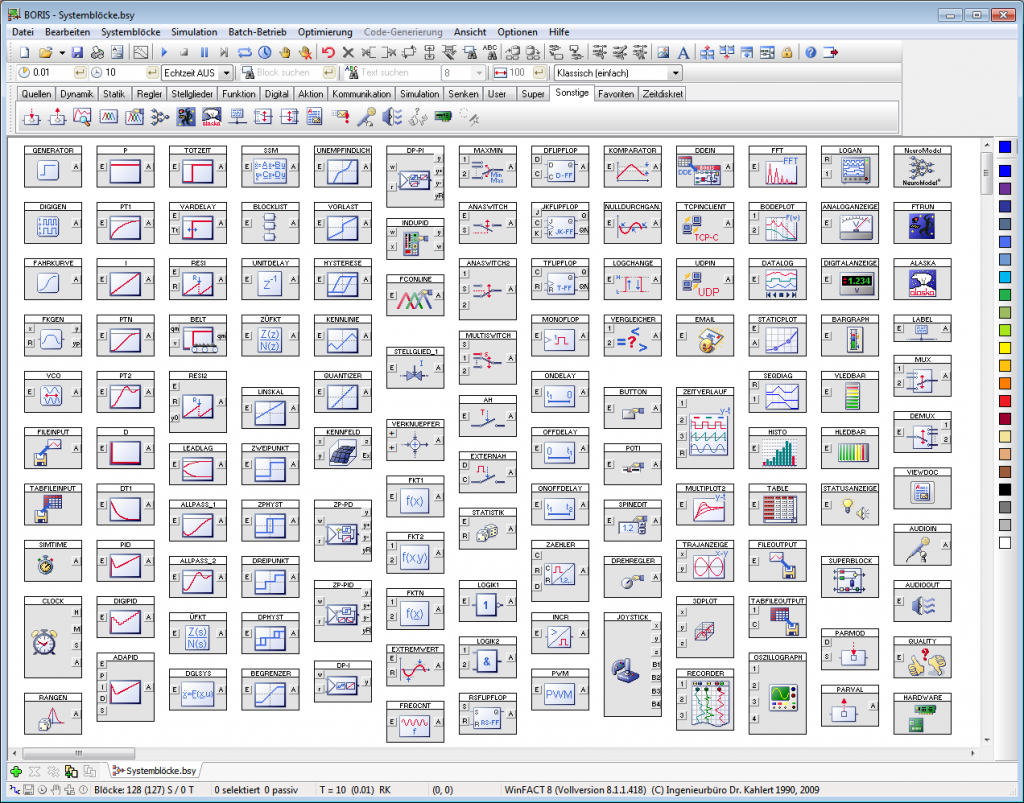
BORIS offers an extensive library including all types of system blocks which are classified into various groups:
-
- Input blocks (Signal producers etc.)
- Dynamic blocks of first and higer order
- Static blocks (two- and three-point characteristics etc.)
- Actuators
- Functional blocks
- Digital modules
- Interactive blocks
- Control elements
- Superblocks
- User-written blocks (User-DLLs)
The following screenshot gives an expression of the BORIS system block library.
The parameters of the system blocks are set via comfortable input masks. The parameters of most system blocks can also be changed during the simulation process.
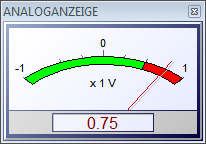
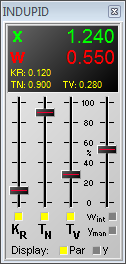
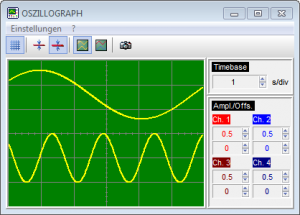
For the visualization of simulation results or measured data and for the interactive control of the simulation process BORIS offers numerous virtual instruments and so-called interactive blocks. As a result of these block types the user gets a feeling of sitting “in a real lab” instead of simulating “only” with a PC – a very important effect especially in the field of training and education! For a real time process interface BORIS offers specific block types which are activated if the corresponding hardware is connected.
The following screenshot shows some typical virtual instruments and interactive elements.
Superblocks and user-defined blocks
The system block library of BORIS can be extended by user specific blocks. Two different block types are available: Superblocks and user-written blocks, so-called User-DLLs.
Superblocks are realized by grouping two or more system blocks to one new block, which now “hides” his inner blocks and connections. By this way it is possible to create reusable modules that can be imported in other simulation structures in as many copies as necessary. Superblocks themselves can also contain other superblocks in any depth.
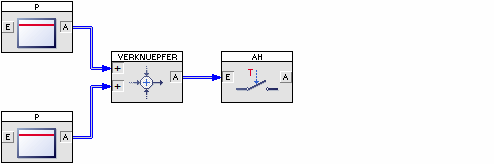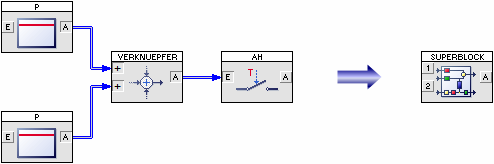
In contrast to superblocks the function of a user-defined block – a User-DLL – is characterized by the user himself. These User-DLLs may be written in any Windows-IDE (C, C++, Delphi, Visual Basic, …) that is able to generate Dynamic Link Libraries. In this way not only pure functional system blocks can be written but also blocks with simple or complex process visualization features (see e. g. our Courses and plant models).
Optimization of System Parameters
As an ideal add-on for the simulation module BORIS we offer the optimization module, which enables the automatic numerical optimization of system parameters (e. g. parameters of a PID-controller) based on a user-defined performance criterion. For the optimization process extremely efficient parameter optimization strategies based on genetic algorithm (evolutionary strategies) are used.
Videos
Downloads
| WinFACT 2016-demo version, as at April 4th, 2017 |
Documentations and product information
| WinFACT 2016-Product overview (German) |